In today’s fast-paced world, technology is constantly evolving, and one of the most transformative innovations in recent years is stereolithography, also known as SLA 3D printing. This groundbreaking technology has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled precision and versatility. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of stereolithography, exploring its history, working principles, applications, and the exciting future it promises.
The Genesis of Stereolithography

Invention of SLA
Stereolithography, or SLA, was invented in the early 1980s by Chuck Hull, an American engineer and entrepreneur. Hull’s pioneering work laid the foundation for what we now know as 3D printing. His invention was a game-changer, allowing for the creation of three-dimensional objects layer by layer, a concept that seemed like science fiction at the time.
How SLA Works
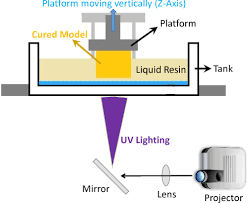
SLA operates on a simple yet ingenious principle. It uses a UV laser to solidify liquid resin layer by layer, gradually building the desired object. The resin hardens when exposed to the laser’s precise beams, and the build platform lowers with each layer’s completion. This process continues until the entire object is formed.
Applications of Stereolithography
Rapid Prototyping
One of the primary applications of SLA is rapid prototyping. Engineers and designers use it to create prototypes of products quickly and cost-effectively. This ability to turn ideas into physical models in a matter of hours has accelerated product development across industries.
In the medical field, stereolithography has been a game-changer for creating custom implants, prosthetics, and dental devices. The technology allows for precise, patient-specific designs, enhancing the quality of care and patient outcomes.
Aerospace Advancements
The aerospace industry has embraced SLA for creating intricate and lightweight components. This not only reduces the weight of aircraft, leading to fuel efficiency but also ensures the structural integrity of these components.
Art and Jewelry
Artists and jewelers have also harnessed the power of SLA to craft intricate and highly detailed pieces. The precision offered by stereolithography enables the creation of complex designs that were once unimaginable.
Advantages of Stereolithography
Unmatched Precision
SLA boasts unmatched precision, with layer thicknesses often measured in microns. This level of accuracy is crucial in fields like medicine and aerospace, where the margin for error is minimal.
Material Variety
Another advantage of SLA is the wide range of materials available for printing. From tough and durable plastics to flexible and bio-compatible resins, there’s a material for every application.
Complex Geometries
Stereolithography can produce objects with intricate and complex geometries that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods.
The Future of Stereolithography
As technology continues to advance, the future of stereolithography looks promising. Researchers are exploring new materials, faster printing methods, and applications in fields we haven’t even imagined yet. With its ability to bring ideas to life with precision and speed, SLA 3D printing is set to shape industries for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, stereolithography has emerged as a transformative force in the world of manufacturing. Its precision, versatility, and ever-expanding applications make it a cornerstone of modern industry. As we look to the future, we can only anticipate the remarkable innovations that will be achieved through this groundbreaking technology.